Organizations have plans in place for protecting their most sensitive data, including financial data. While many organizations pivoted to a remote work environment during the pandemic, their cybersecurity plans may not have kept up with the work environment shift.
Whether working from home or in the office, employees may invite a threat inside the organization through their behaviors, such as using a weak password (which is easily guessed) or downloading software that contains malicious software (i.e., malware).
Read on to discover the most common threats for financial data and how AI can protect your organization’s data and your client base’s personal identifiable information.
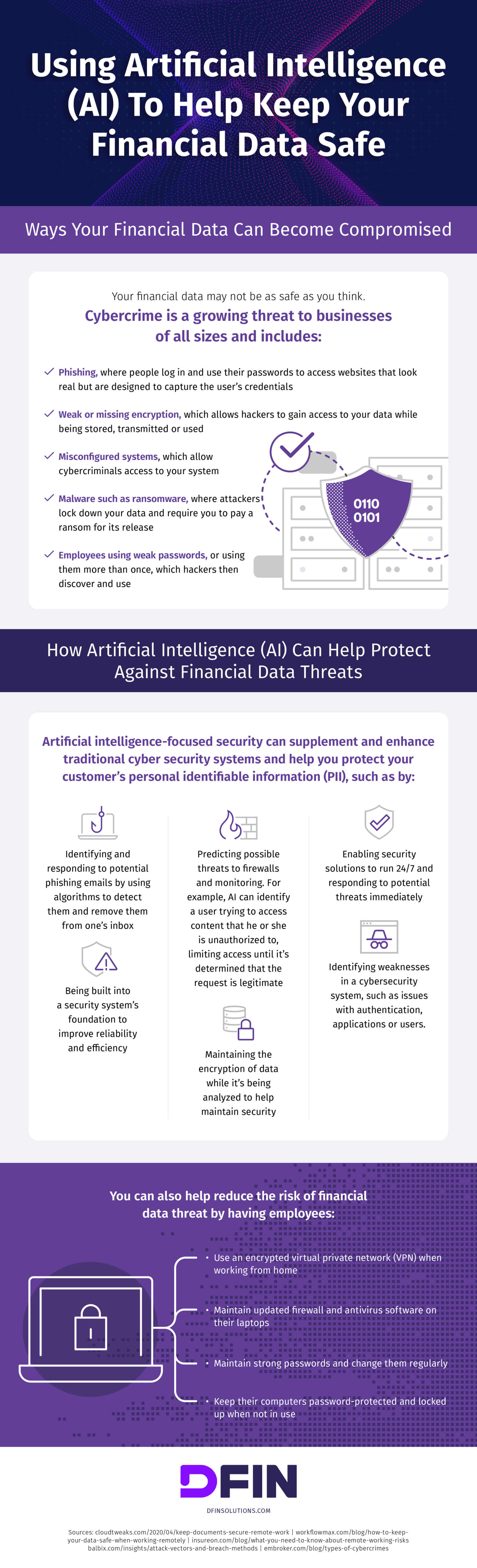
Ways financial data may be compromised
These common vulnerabilities lead to compromised financial data:
- Malware: Once installed, the malware runs on the computer, capturing sensitive data for exploitation by hackers.
- Ransomware: A type of malware, ransomware locks down business assets until a cash ransom is paid by the business.
- Phishing: Phishing emails impersonate legitimate messages in an attempt to gain access to user credentials. Learning to recognize phishing emails is the first step to decrease vulnerability.
- Weak or recycled passwords: Using the same password across sites or using a weak password (such as 123456) is one of the biggest causes of compromised data. Hackers easily guess the password, then impersonate a legitimate user to gain access to enterprise assets.
- Insufficient encryption: Encryption protects data during transfers, so an attacker cannot intercept raw data. If encryption is missing or weak, hackers can grab unencrypted data, such as account numbers.
- System misconfiguration: System misconfigurations leave open doors for hackers to obtain the information they can exploit, such as access credentials.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi: Hackers may be able to scrape legitimate credentials from remote workers who use unsecured Wi-Fi to connect to the server and then penetrate the system to compromise financial data.
Each of these vulnerabilities can be fixed to reduce the risk of a hacker gaining access to critical financial data. By educating employees on the changing face of threats, such as phishing or malware, and adopting stronger password requirements, businesses can lower the role that employees play in ushering a threat. By investing in the right technologies to deter threats, monitor systems, and mitigate attacks, businesses can further reduce the chance of data breaches. Many of the strongest cybersecurity tools use AI to keep business systems safe and protect consumer data.
How AI can protect customer data
To understand how AI supports stronger cybersecurity, consider how hackers and cybersecurity experts are locked in a game of cat and mouse. As cybersecurity experts develop systems capable of detecting and responding to threats faster, locking out the hackers, the attackers change their approaches to stay one step ahead of the software.
It’s challenging for anyone cybersecurity software to keep up with all the new tactics hackers try and each of the new access points they might exploit to gain access. Employees working remotely may be using their personal Wi-Fi networks and devices while working from their home with an array of connected smart home devices — each of which offers a way into the system for a determined hacker.
AI solutions are not intended to replace traditional threat detection and mitigation tools. Instead, they supplement these tools for robust protection from the latest generation of threats. AI solutions often take a sandbox approach by redirecting potentially suspicious activity to a contained environment for further analysis. This near-instantaneous approach prevents the hacker from getting to the goodies. Since these systems operate continuously (unless they’re turned off at the source), companies enjoy 24/7 protection.
Because AI cybersecurity tools are powered by machine learning, they’re able to evolve alongside the hackers. The tools also draw on predictive and pattern-recognition capabilities to quarantine threats to the system. In acting proactively when there’s suspicious activity, these systems provide fast notification to IT personnel, who can manually review the activity. This way, bad actors are kept out while legitimate users are granted access to the system.
Be sure to read the accompanying resource created by Donnelley Financial Solutions. It illustrates the ways that AI can help to keep business financial data safe, as well as best practices employees, can adopt to reduce the risk of data threats. Ultimately, the best approach to protect business data combines the right cybersecurity monitoring tools with employee education. Working together, these two streams of action reduce the areas of risk to the smallest possible target.